You deployed Cluster Autoscaler. Your pods are pending. But the nodes aren't scaling up.
What gives?
Spoiler: It's rarely the autoscaler’s fault.
In production, tiny misconfigurations, resource mismatches, and scheduling quirks silently block autoscaling—without a single error log.
This guide is your complete blueprint to debug, fix, and future-proof autoscaling failures with confidence.
How Cluster Autoscaler Really Thinks
Most engineers believe:
"If pods are pending, autoscaler should scale up. Simple."
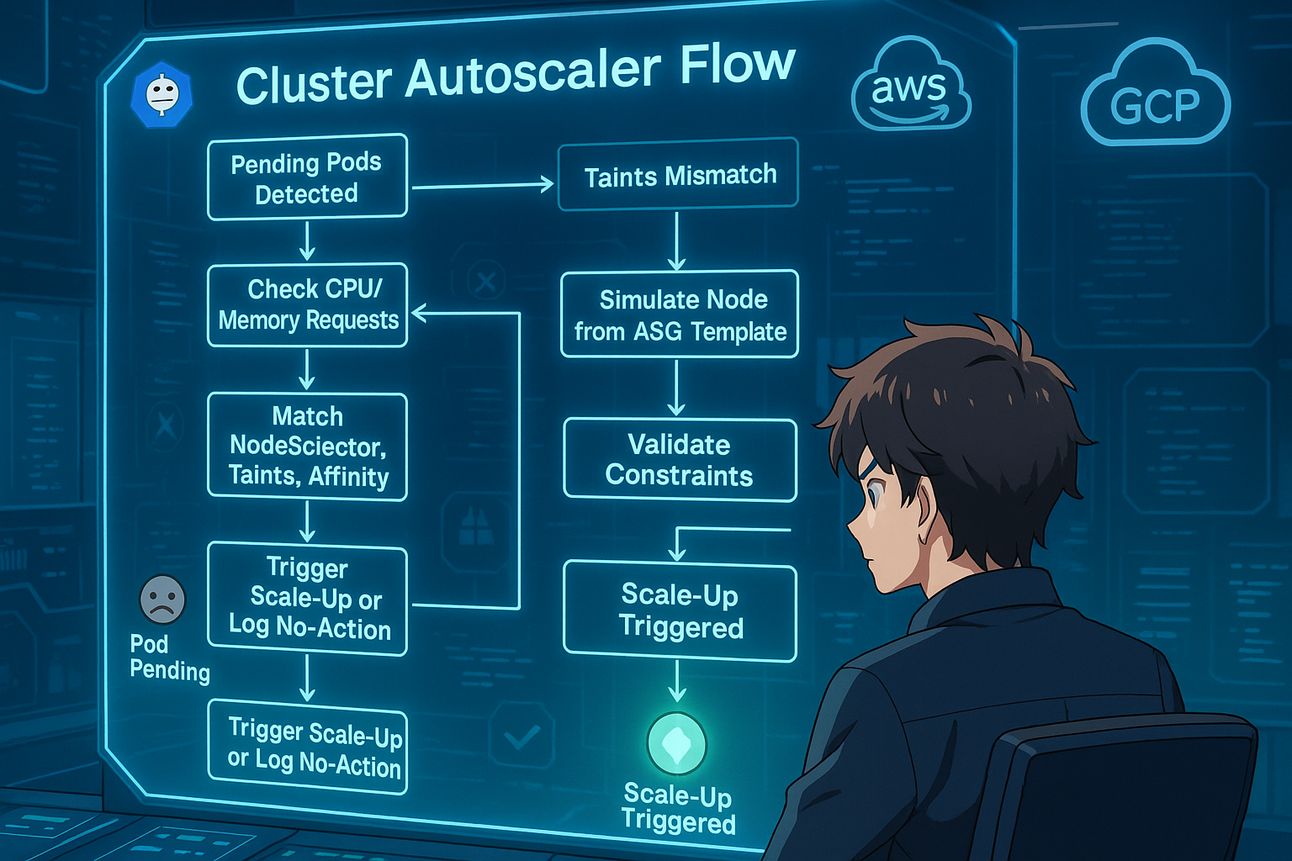
Wrong. Cluster Autoscaler goes through a multi-step logic pipeline:
Is there a pending pod?
Does the pod have valid CPU/memory
requests?Can a new node (based on existing ASG configs) actually run this pod?
Any
nodeSelector,affinity,taints,PDB, or misconfigs blocking scheduling?If yes → Simulate node → Trigger scale-up.
If any of these fail, autoscaler quietly gives up.
Top Reasons Cluster Autoscaler Doesn’t Scale (with Fixes)
Let’s decode the hidden traps. Each one comes with real fixes and curious behaviors.
1. No Resource Requests = No Scaling
If your pod doesn’t request CPU/memory, autoscaler ignores it.
Fix:
resources:
requests:
cpu: "200m"
memory: "256Mi"
2. nodeSelector or affinity Is Too Strict
You’re asking for nodes that don’t exist in your ASG. Autoscaler can’t simulate a valid node → no scale.
Fix: Ensure nodeSelector matches ASG instance labels or node pool metadata.
3. PodDisruptionBudget Blocks Scale-In
Your cluster won’t scale down if PDBs are set too aggressively.
Insight: Even empty clusters won’t scale down if PDB thinks evicting a pod violates budget.
4. Max Nodes Limit Reached
Your ASG’s maxSize is set to 5, but you need 7 nodes.
Fix:
aws autoscaling update-auto-scaling-group --max-size 10 ...
5. Taints Without Tolerations
If your nodes are tainted (e.g., GPU nodes) but pods don’t tolerate them, autoscaler won’t scale even if capacity is available.
Fix: Add tolerations to your pod spec to match node taints.
For AWS:
k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/enabled: true
k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/<cluster-name>: owned
Fix: No tag = No autoscaling.
7. Anti-Affinity Rules Prevent Scheduling
Strict anti-affinity = autoscaler can't find a layout to satisfy your policy.
Fix: Review anti-affinity rules and test node-pod layouts manually.
8. Volume Attach Constraints (Zonal Traps)
Your pod uses a PVC in zone-a, but autoscaler is trying to create nodes in zone-b. Scaling silently fails.
Fix: Use topology-aware storage class or restrict node pool to specific zones.
9. Custom PriorityClass Blocks Lower Priority Pods
High-priority pods always scale. Low-priority ones can be starved if capacity isn’t guaranteed.
Fix: Use correct priorityClassName and observe preemption behavior.
10. Mixed Instances & Launch Template Drift
Using mixed instance policies? Autoscaler simulates node type that fails to launch due to LT mismatch.
Fix: Re-sync Launch Template, verify instance types.
Observability: Metrics You Should Be Watching
Use Prometheus + Grafana or CloudWatch to visualize:
Pending Pods (
kube_pod_status_scheduled)Autoscaler Events (
cluster_autoscaler_unschedulable_pods_count)Node Group Scaling Actions
Pro tip: Alert if pod pending time > 60s without node add event.
Real Cluster Autoscaler Logs & What They Really Mean
Log 1: Pod Unschedulable
I0706 10:42:12.134012 1 scale_up.go:531] No schedulable pods
Fix: Add CPU/memory requests, check selectors.
Log 2: Max Nodes Reached
I0706 10:42:13.675010 1 scale_up.go:323] No scale-up: max nodes in node group reached
Fix: Raise maxSize for ASG.
Log 3: Could Not Find Node Group
W0706 10:43:10.235010 1 scale_up.go:217] No node group for pod default/my-app-xyz
Fix: Check nodeSelector, affinity, taints.
Terraform: Autoscaler-Ready AWS ASG Setup
1. Tag Your ASGs
tags = [
{
key = "k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/enabled"
value = "true"
propagate_at_launch = true
},
{
key = "k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/${var.cluster_name}"
value = "owned"
propagate_at_launch = true
}
]
2. IAM Permissions
statement {
actions = [
"autoscaling:DescribeAutoScalingGroups",
"autoscaling:SetDesiredCapacity",
"autoscaling:TerminateInstanceInAutoScalingGroup",
"ec2:DescribeLaunchTemplateVersions"
]
resources = ["*"]
}
YAML Before & After: The Fix That Saves You Hours
Bad Pod YAML
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: my-app
spec:
containers:
- name: app
image: myapp:v1
nodeSelector:
instance-type: gpu
Good Pod YAML
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: my-app
spec:
containers:
- name: app
image: myapp:v1
resources:
requests:
cpu: "250m"
memory: "512Mi"
tolerations:
- key: "app-node"
operator: "Equal"
value: "true"
effect: "NoSchedule"
nodeSelector:
app-node-group: "true"
Cheatsheet Recap: What to Check
What to Check | Tool/Command |
|---|---|
Pod requests missing? |
|
Autoscaler logs? |
|
Node group tags valid? |
|
Simulated node mismatch? | Check Launch Template vs workload requirements |
PVC zone mismatch? |
|
Debug Like an SRE, Scale Like a Pro
When autoscaling breaks, most engineers dig into logs. But the real win?
Understand autoscaler’s logic like a system, not a tool.
Use this guide to fix issues faster, design better infra, and build self-healing clusters that scale smartly , not just automatically.